Why CPU Clock Speed Unreliable Measure of Computer Performance
If you are shopping for a new tablet, phablet, laptop or desktop computer, CPU clock speed is probably less important criteria than it used to be. The “CPU speed” in gigahertz, or GHz was once a simple way to compare the performance of computers.
The central processor's clock speed rate is simply the number of clock cycles the CPU can complete every second. For example, a clock rate of 1.5 GHz means the CPU or multiple CPUs, can complete 1,500,000,000 clock cycles per second.
But modern CPUs are now highly efficient and other things have more affect on their performance. It now depends of what the processor can do within each clock cycle. This partly depends on it's design, amount of memory available to it and how efficiently the memory is accessed and used.
Many CPU have inbuilt cache memory. It also depends on hard disk access and the efficiency of a number of peripherals. Various computers use different CPU designs, and so speed is only one of many aspects to consider.
This article discusses the pros and cons of using CPU to rate and compare the performance of computer devices.

Modern CPUs no longer operate at a fixed at a single speed, due to power consumption, battery life and heating issues. Instead, the CPU speed drops when idle or runs slowly when doing minimal work. The CPU speed ramps up towards the maximum speed to meet higher demands and loads. But it then switches back to slower rates once the job is donne. In some cases, cooling and battery demand may be added considerations when choosing smartphones, tablets and tablets.
The supportive hardware devices are also very important when it comes to the general performance of your computer or mobile device. The type and speed of the disc access are very important. The speed and performance of the video card is also very important. The amount of RAM available and its access speed can affect performance.
Using Benchmarks to Measure and Compare Computer Performance
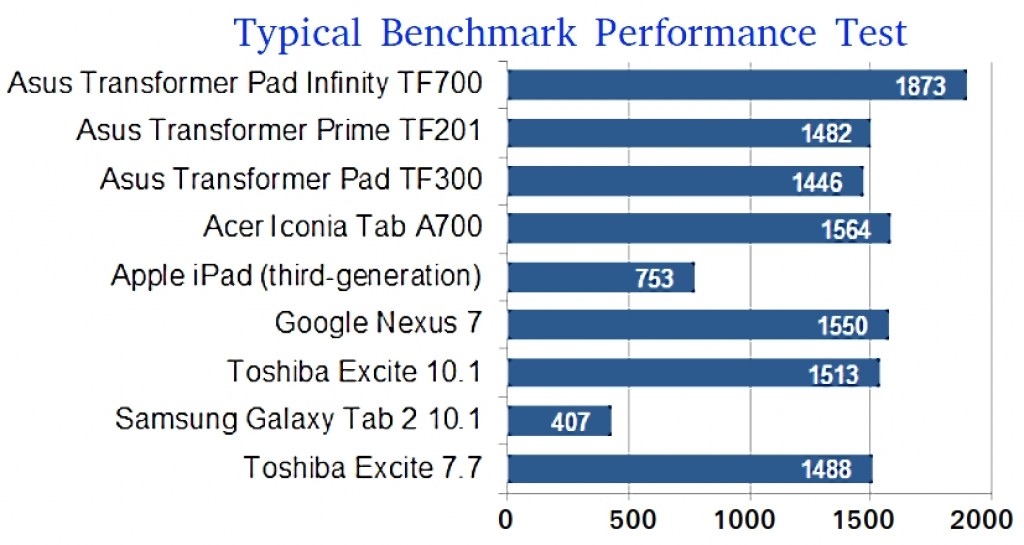
In computing, a benchmark is a computer program, or set of programs that are run specifically to measure relative performance, usually in terms of the speed it takes to complete the task. An example is shown in the image.
Benchmarks may be mathematical operations but can also be more complicated operations with a defined output.
Benchmarks provide a way of testing the entire computer system nut just the CPU.
Various test suites are available for doing these tests.